Buccal fat, a term that has recently surged into popular conversation thanks to aesthetic trends and celebrity transformations, refers to a specific pocket of fat located in the mid-face. While it plays a crucial role in facial contouring and function, its importance extends beyond cosmetic concerns. This article delves into the anatomy, purpose, aesthetic considerations, surgical removal procedures, and the broader implications of buccal fat in health and beauty.
Understanding buccal fat is essential not only for those considering cosmetic enhancements but also for appreciating the natural architecture of the human face.
What Is Buccal Fat?
Anatomical Overview
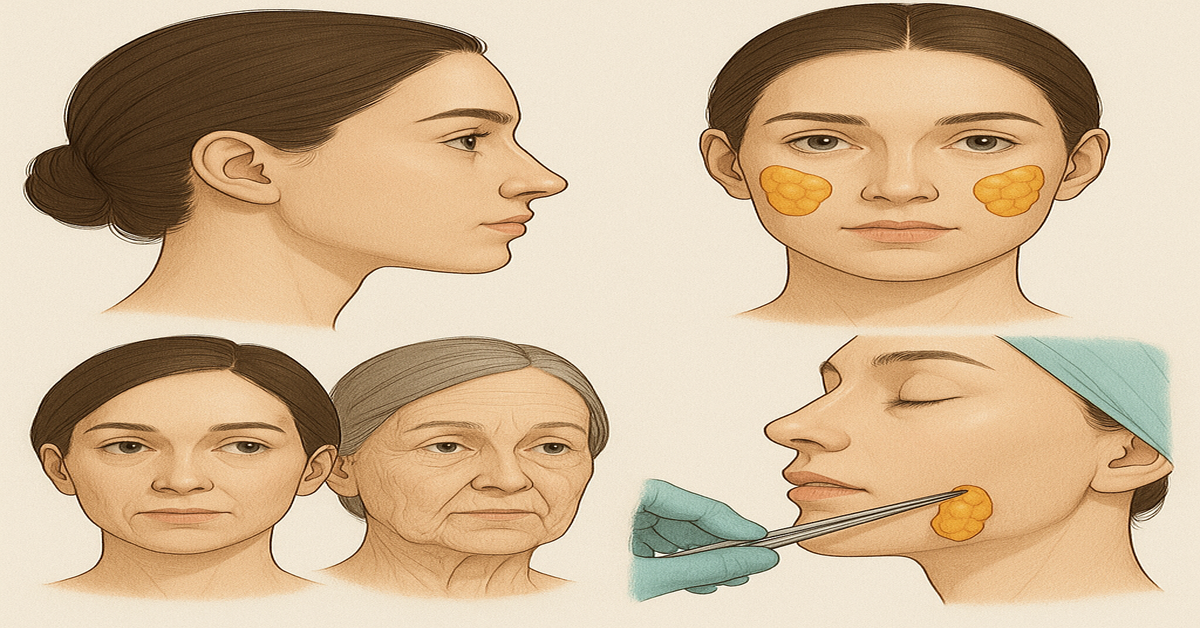
The buccal fat’s pad is a rounded mass of fat located deep within the cheeks, between the facial muscles. It sits between the buccinator muscle (responsible for helping with chewing) and other muscles responsible for facial expressions.
Buccal fat’s is distinct from subcutaneous fat (the layer of fat just beneath the skin) and serves a unique functional purpose. Everyone has buccal fat’s, although the amount and distribution can vary greatly among individuals.
Purpose of Buccal Fat
Buccal fat’s provides cushioning to protect facial muscles during chewing and talking. It also contributes to a youthful and full appearance of the mid-face. In infants and young children, buccal fat’s is particularly pronounced, helping with suckling.
As people age, changes in buccal fat’s can impact facial aesthetics—sometimes leading to a hollow or sunken look, while in others it remains prominent, leading to a rounder, softer appearance.
The Role of Buccal Fat in Facial Aesthetics
Youthful Fullness
Full, round cheeks are often associated with youth and vitality. Buccal fat’s supports this look by providing volume in the mid-face area. Loss of buccal fat’s over time can contribute to signs of aging, including sagging skin and a gaunt appearance.
Influence on Facial Shape
Individuals with prominent buccal fat’s pads may have a rounder or “baby-faced” appearance, while those with less pronounced buccal fat’s might have more angular and defined features. As trends shift toward favoring high cheekbones and chiseled jawlines, some seek to modify their buccal fat’s to achieve these aesthetics.
Buccal Fat Removal: An Overview
What Is Buccal Fat Removal?
Buccal fat’s removal, also known as cheek reduction surgery, is a cosmetic procedure that involves the surgical extraction of a portion of the buccal fat’s pad. The goal is to create a slimmer, more contoured facial appearance.
How the Procedure Is Done
The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia or mild sedation. A small incision is made inside the mouth, minimizing visible scarring. The surgeon then carefully teases out a portion of the fat pad before closing the incision with sutures.
Recovery Time
Recovery from buccal fat’s removal is relatively quick compared to other cosmetic surgeries. Most patients experience swelling and minor discomfort for a few days to a few weeks. Normal activities can usually be resumed within a week, although full results may take several months to appear as swelling subsides.
Pros and Cons of Buccal Fat Removal
Advantages
- Enhanced facial contours: Highlights cheekbones and jawline.
- Permanent results: Once removed, buccal fat’s does not regenerate.
- Subtle scarring: Incisions inside the mouth leave no external scars.
Disadvantages
- Potential for overcorrection: Excessive removal can lead to an overly hollow, aged appearance.
- Irreversibility: Once buccal fat’s is removed, it cannot be restored naturally.
- Not suitable for everyone: Individuals with already lean faces may not be good candidates.
Buccal Fat and Aging
Natural Changes Over Time
As part of the natural aging process, buccal fat’s tends to diminish, leading to a loss of facial volume. This can create a hollow, older look, especially in individuals who are already lean.
For this reason, many cosmetic surgeons advise caution when considering buccal fat’s removal. Premature removal in younger patients may accelerate the appearance of aging later in life.
Alternatives to Surgery
Instead of removing buccal fat’s, some individuals choose non-invasive options such as facial fillers to enhance contour or improve symmetry without surgical risks.
Buccal Fat Enlargement: A Rare Concern
Medical Conditions
While most attention around buccal fat’s centers on its removal, abnormal enlargement of the buccal fat’s pads can occur due to specific medical conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome or localized lipomas.
Treatment Options
Treatment typically focuses on addressing the underlying medical condition. In rare cases, surgical removal may be recommended for functional or aesthetic reasons.
Buccal Fat in Cultural Context
Historical Beauty Standards
Historically, plump, full faces were often seen as indicators of health and prosperity. Only recently have slender, angular facial features become a widespread beauty ideal, driven largely by fashion and celebrity culture.
Modern Trends
The rise of buccal fat’s removal corresponds with broader trends in cosmetic surgery favoring dramatic contouring, sculpted cheekbones, and sharper jawlines. However, beauty standards are fluid, and what is considered desirable today may shift in the future.
Risks and Considerations Before Surgery
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Given the delicate nature of buccal fat’s removal, it is critical to select a board-certified plastic surgeon or facial surgeon with experience in facial anatomy and aesthetic balance.
Comprehensive Consultation
A thorough consultation should include:
- Discussion of goals and expectations
- Evaluation of facial structure and fat distribution
- Review of potential risks and complications
Psychological Factors
Candidates should consider their motivations carefully. Cosmetic procedures can offer enhancement but should not be seen as cures for deeper self-esteem issues.
Buccal Fat in Reconstructive Surgery
Functional Importance
In reconstructive facial surgery, preserving or reconstructing buccal fat pads can be crucial for restoring symmetry, function, and aesthetics, especially after trauma or tumor removal.
Innovative Techniques
Recent advances have allowed surgeons to use fat grafting techniques to replace lost buccal fat’s, helping patients recover a natural, youthful appearance after injury or illness.
Conclusion
Buccal fat’s plays a vital role in both the function and appearance of the human face. While trends in aesthetics have spotlighted buccal fat removal as a means to achieve sharper facial contours, it is important to approach the decision with careful consideration. Understanding the anatomy, natural aging processes, and potential long-term effects is essential before choosing surgery.
Buccal fat is not merely a cosmetic concern; it is a fundamental part of facial health and beauty. Whether preserving it for youthful fullness or modifying it for enhanced definition, respecting its role ensures that any intervention supports both appearance and overall facial harmony.
FAQs
1. Can buccal fat grow back after removal?
No, once buccal fat is surgically removed, it does not regenerate. However, overall facial fat can fluctuate with weight changes.
2. Who is a good candidate for buccal fat removal?
Ideal candidates are individuals with full cheeks who desire a more contoured facial appearance and who have realistic expectations about the results.
3. Are there non-surgical alternatives to buccal fat removal?
Yes. Techniques such as facial sculpting with dermal fillers or targeted fat reduction using radiofrequency or ultrasound therapy can enhance facial contours non-surgically.
4. What are the potential complications of buccal fat removal?
Risks include infection, facial asymmetry, nerve injury, prolonged swelling, and dissatisfaction with the aesthetic outcome.
5. How long does it take to see the final results of buccal fat removal?
While initial improvements are noticeable within a few weeks, full results can take three to six months as swelling completely resolves.
6. Is buccal fat removal popular among men?
Yes, buccal fat removal is increasingly popular among men seeking more defined, chiseled facial features. The procedure and recovery are similar across genders.